Coefficient Of Friction Between Rubber And Aluminum

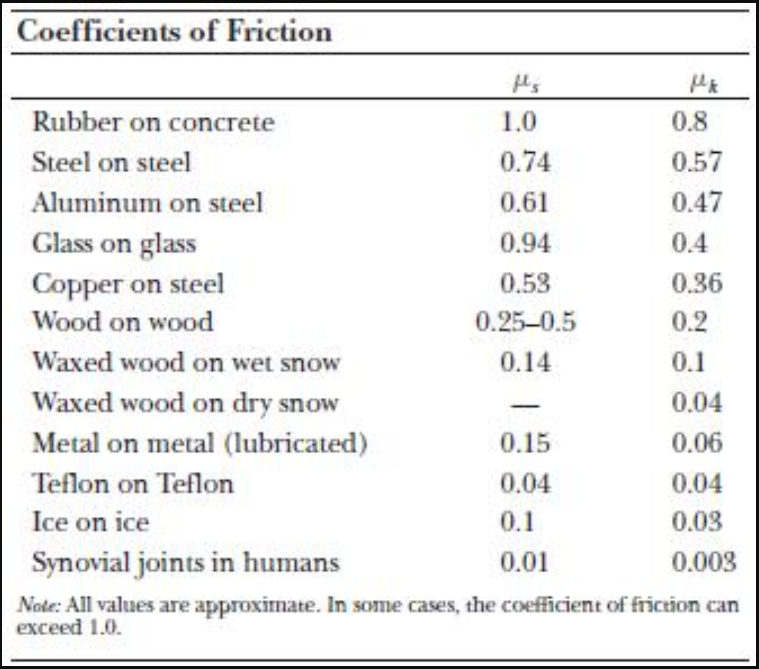
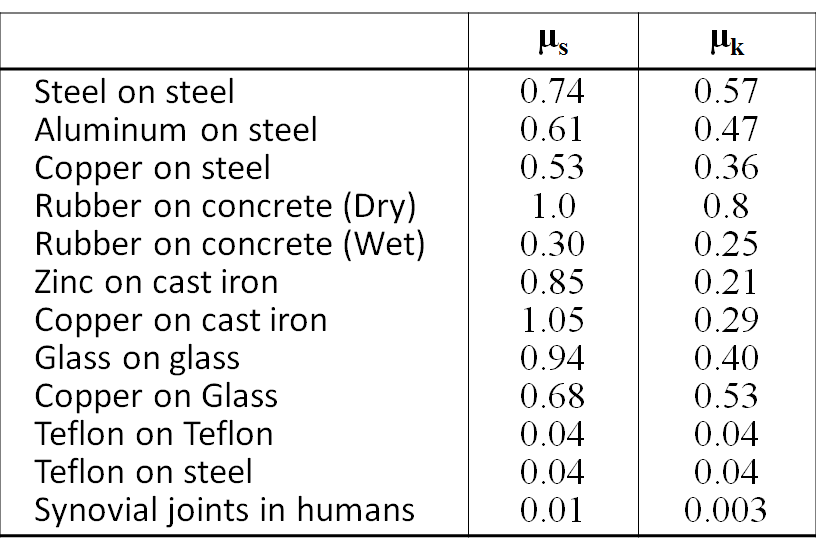
Static and kinetic coefficient of friction.
Coefficient of friction between rubber and aluminum. For rubber on tarmac close to 1 0. The coefficient of static friction typically denoted as μ s is usually higher than the coefficient of kinetic friction. Dry steel dry steel 0 70 0 57 0 80 greasy steel dry steel 0 23 0 16 0 90 greasy steel greasy steel 0 23 0 16 0 90 dry aluminiumdry steel 0 70 0 50 0 85 dry aluminiumgreasy steel 0 23 0 16. Example friction force the friction force of a 100 lb wooden crate pushed across a concrete floor with friction coefficient of 0 62 can be calculated as.
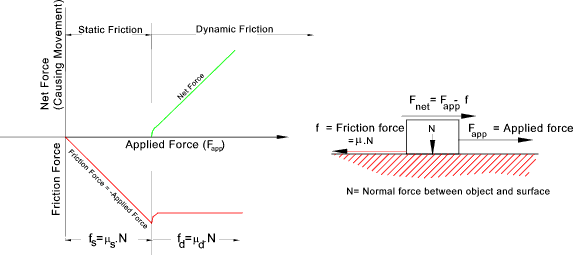
Static friction is friction between two or more solid objects that are not moving relative to each other. Showing the concept of coefficient of friction. It should be noted that there can be significant differences between static friction typically higher and kinetic sliding friction. The friction coefficients considered below are for static friction cases where two solid surfaces in contact with each other are resisting relative lateral motion.
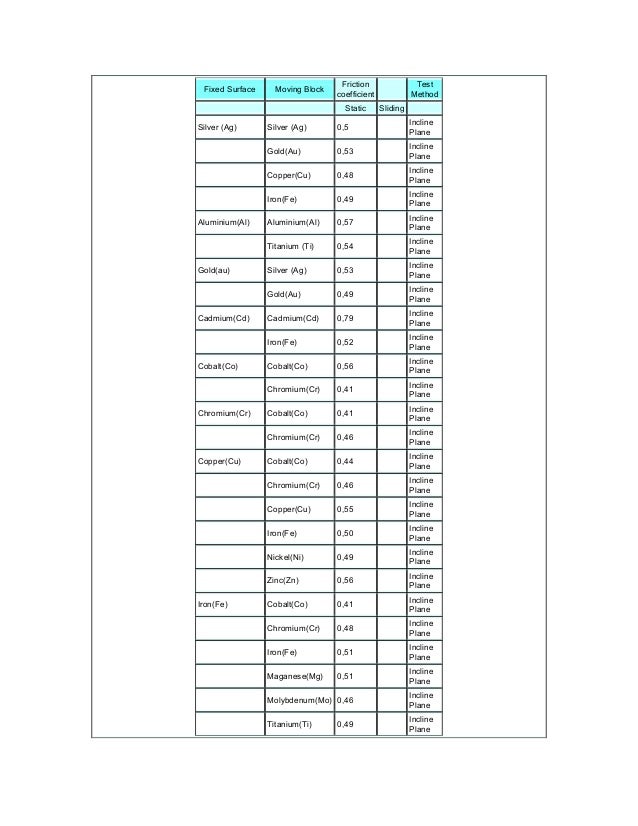
For glass on glass 0 4. However it is possible to find tables in the literature for friction coefficients between various materials. Dynamic coefficient of friction and restitution. 1 2 2 static friction in rubber pad forming processes 3 1 3 static friction and tribological system 3 1 3 1 static friction introduction 3 1 3 2 static friction and tribological system 4 1 4 outline of the dissertation 5 2.
The dynamic coefficient of friction are. Coefficients of friction between materials are best determined through testing. F f 0 62 100 lb 62 lb 1 lb 0 4536 kg. References learn more about contacts.
The static and kinetic friction coefficient values reference table shown in this article will be helpful for finding the cof values of commonly used materials. Example car braking friction force and required distance to stop. Static friction 7 2 1 friction and coefficient of friction 7 2 2 static friction regime 9. The value of μ s is generally higher than the value of μ k for a given combination of materials.
The coefficient of friction is the ratio of a force to a force and hence has no units. Typical values for the coefficient of friction when sliding is occurring i e. A car with mass 2000 kg drives with speed 100 km h on a wet road with friction coefficient 0 2. For example static friction can prevent an object from sliding down a sloped surface.
Where μ s is the coefficient of static friction and μ k is the coefficient of kinetic friction. Static friction results from the normal force of two objects in contact acting opposite the intended motion of one surface against the other. The friction force can be calculated as. Ff 0 62 100 lb 62 lb 1 lb 0 4536 kg example car stopping distance a car with mass 2000 kg drives with speed 100 km h on a wet road with friction coefficient 0 2.