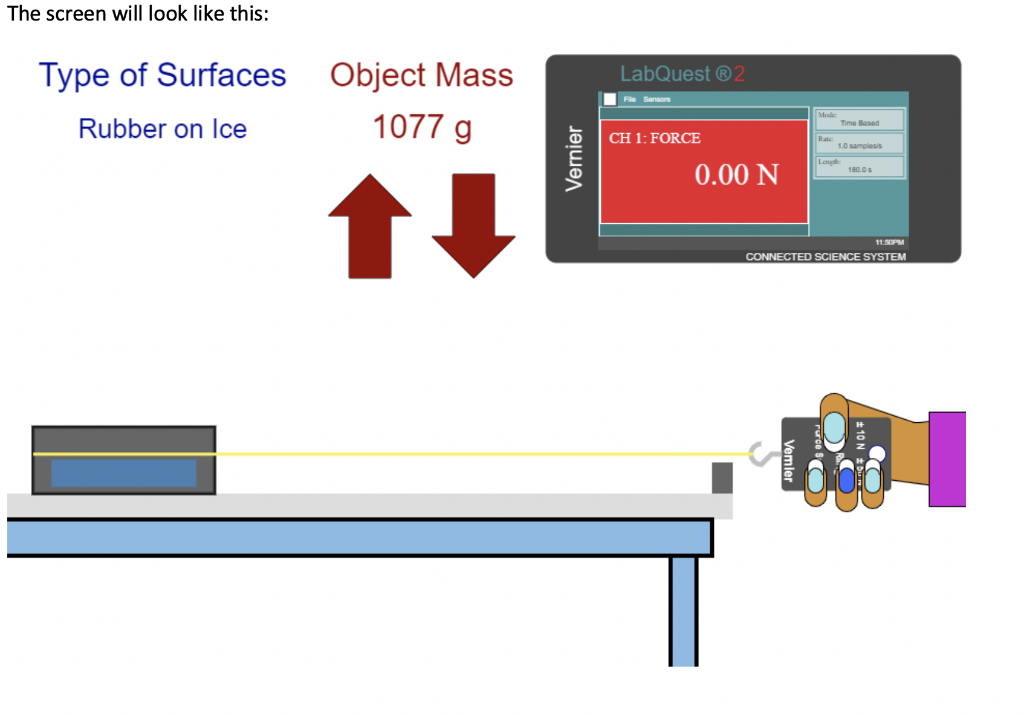
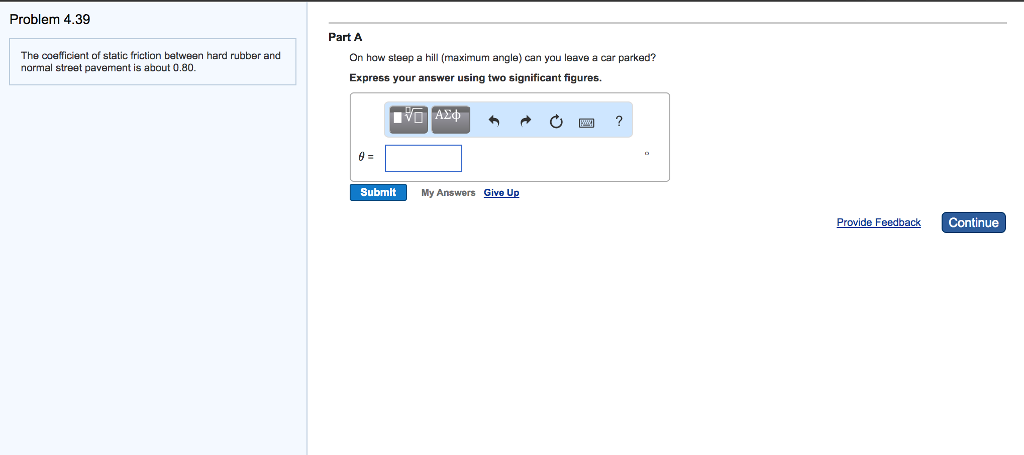
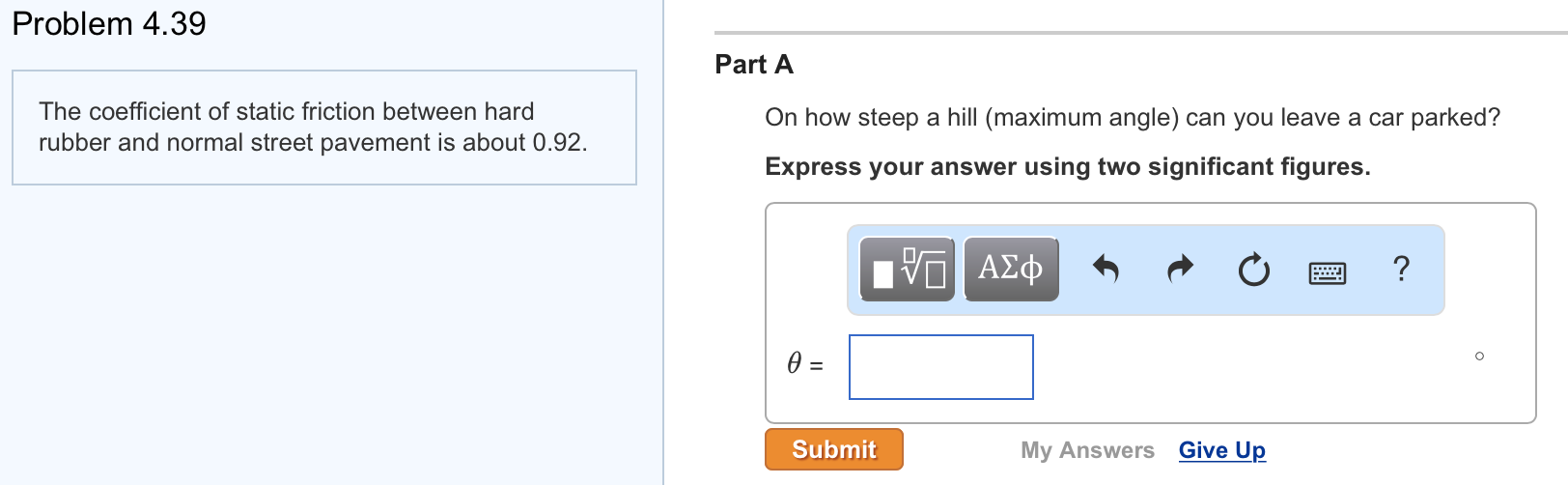
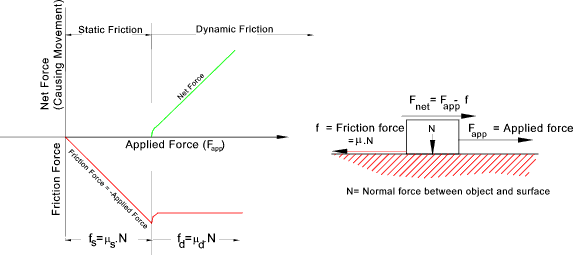
Coefficient Of Kinetic Friction Rubber On Asphalt
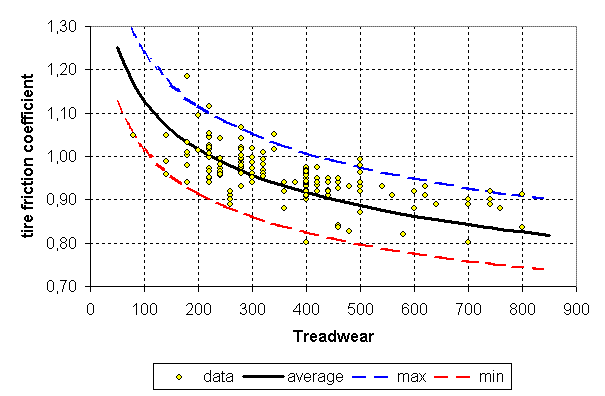
Modern asphalt thin surface course layers with small coarse aggregate sizes which have relatively low texture depth locked wheel friction decreases with speed but not to the extent expected from other hma or pcc surfaces with comparably low macrotexture.
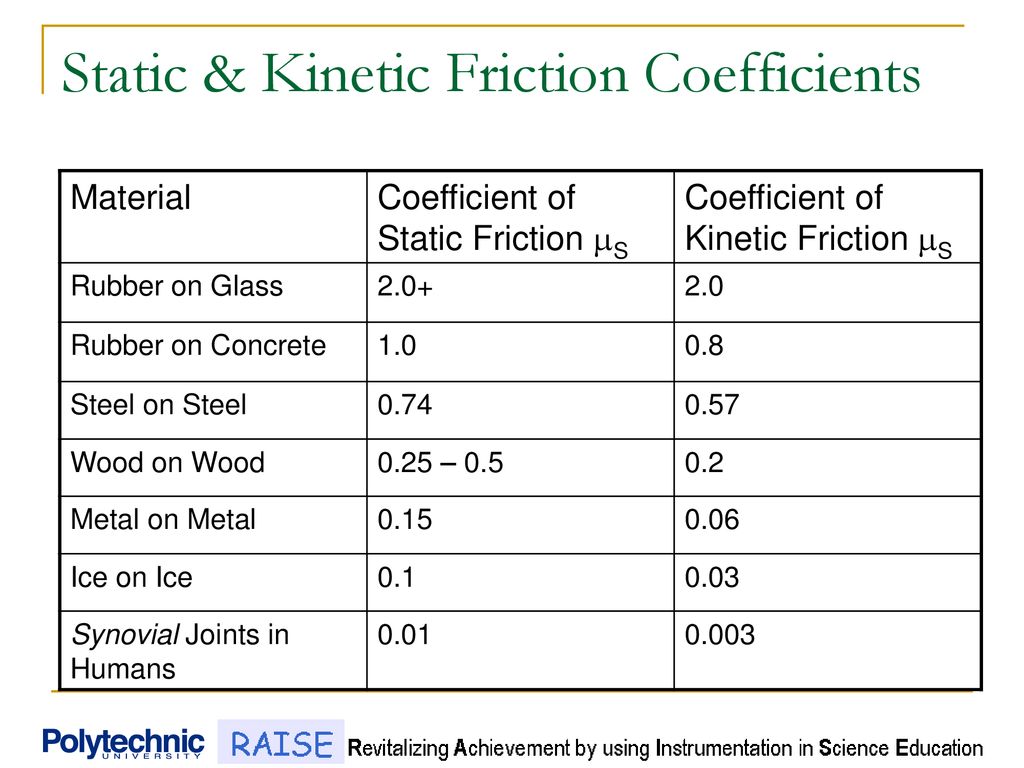
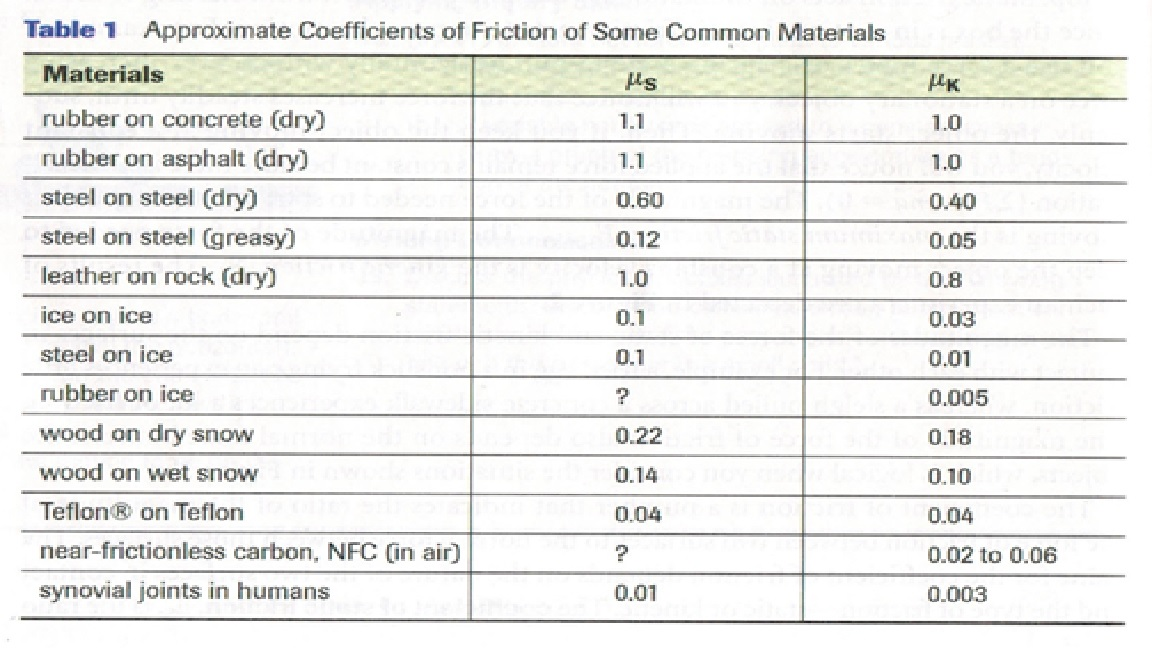
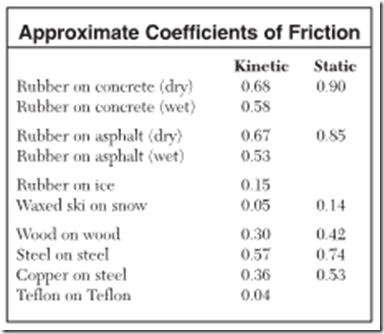
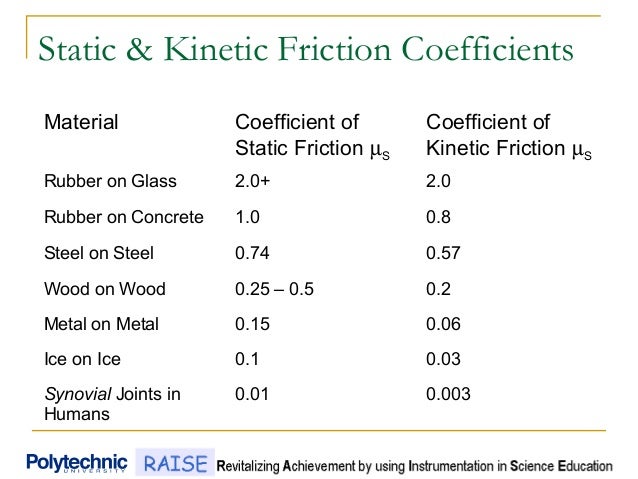
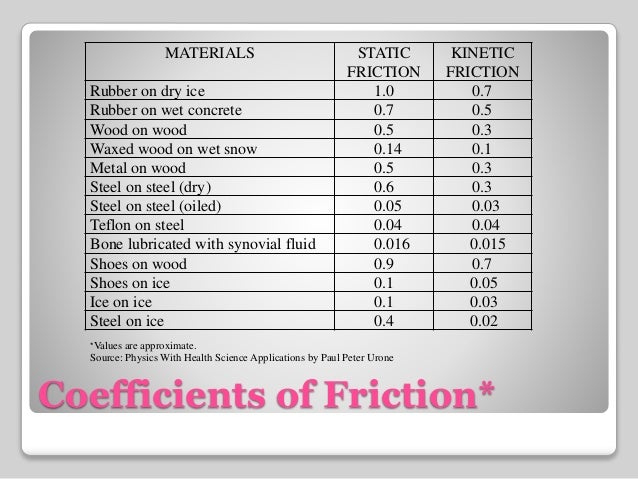
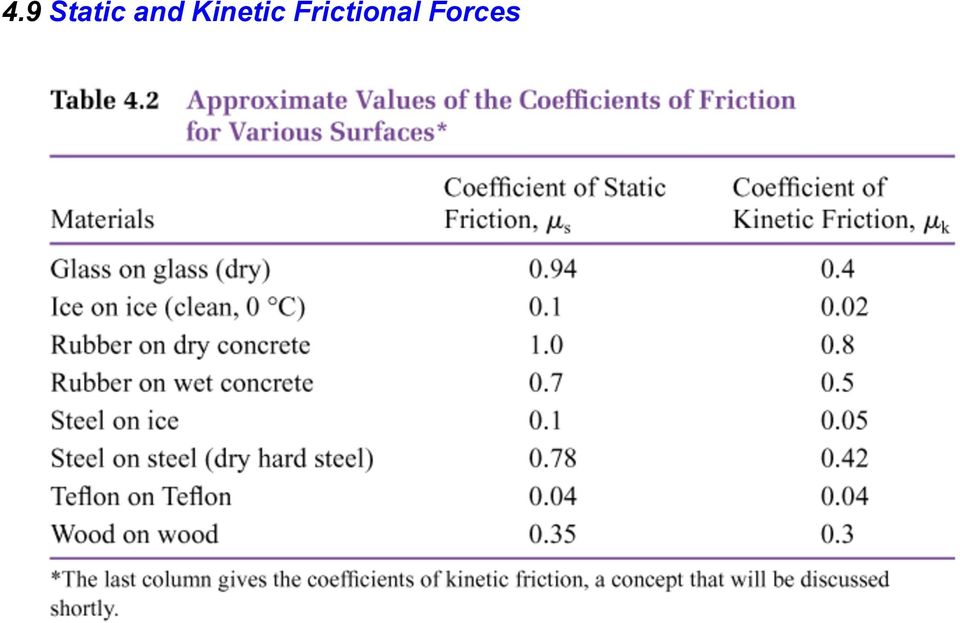
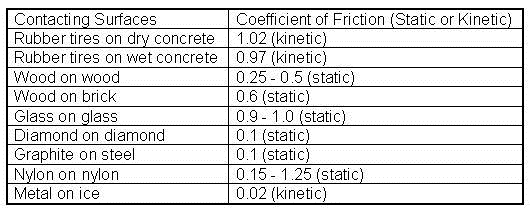
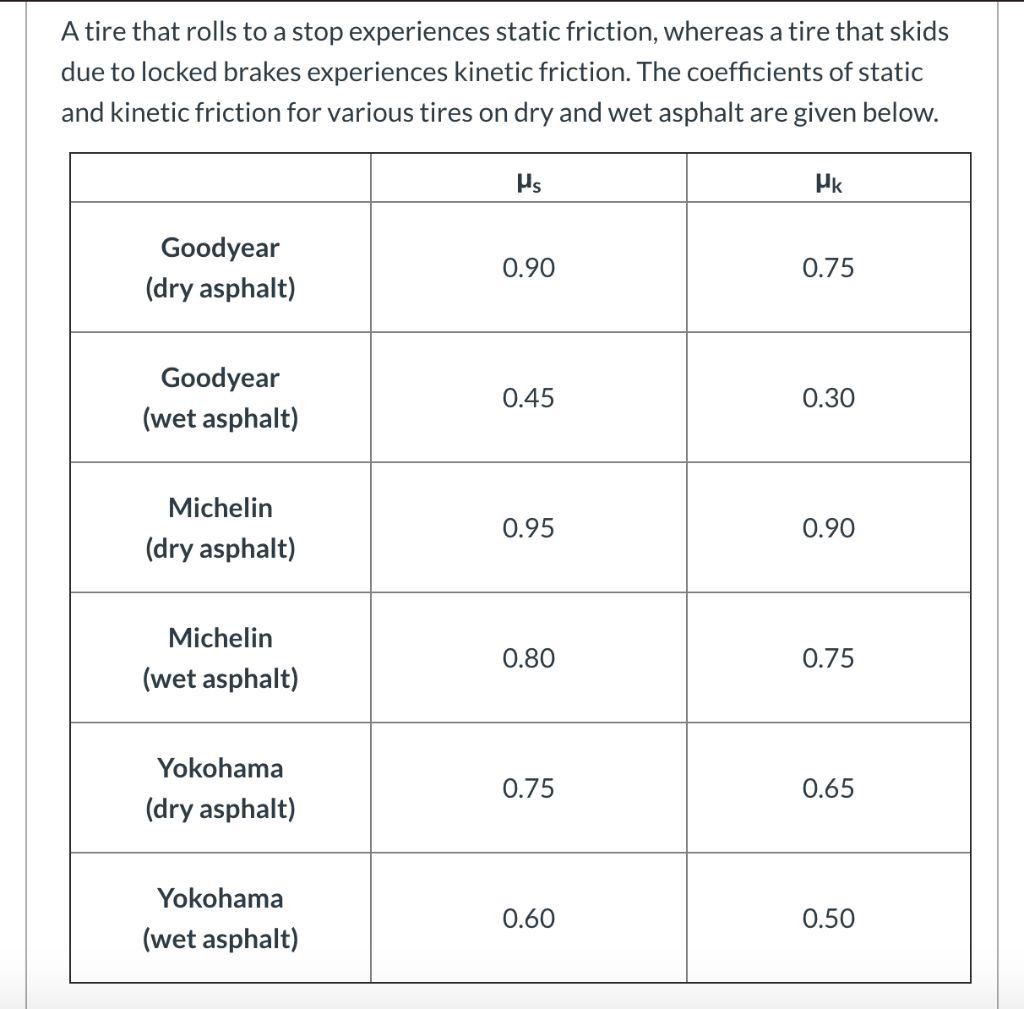
Coefficient of kinetic friction rubber on asphalt. The coefficient of friction of rubber depends upon the surface in contact with the rubber. Static and kinetic coefficient of friction. The static and kinetic friction coefficient values reference table shown in this article will be helpful for finding the cof values of commonly used materials. Rubber on concrete wet 0 58 rubber on asphalt dry 0 68 0 85.
The frictional force can be expressed as. F f frictional force n lb. F f μ n 1. Since friction is a force the unit of the.
Where g is the gravitational acceleration v is the initial velocity when the brakes are applied and f r is the rolling resistance coefficient and was assume to be equal to 0 013. Rubber on asphalt wet. Static coefficients are somewhat higher than kinetic coefficients. N normal force between the surfaces n lb there are at least two types of friction forces.
A common value for k for production car is 0 0000658 s 2 m 2. Static friction is friction between two or more solid objects that are not moving relative to each other. The friction force is the force exerted by a surface when an object moves across it or makes an effort to move across it. Showing the concept of coefficient of friction.
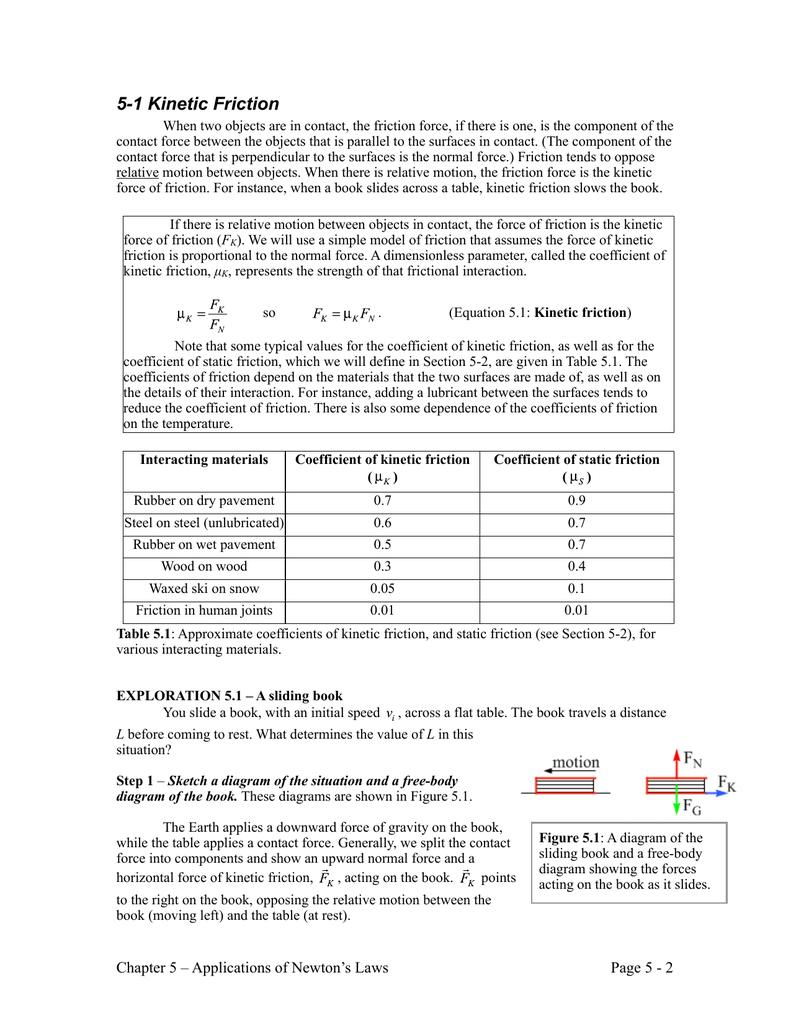
Rubber on concrete dry 0 68. Where f k is the force of kinetic friction μ k is the coefficient of sliding friction or kinetic friction and f n is the normal force equal to the object s weight if the problem involves a horizontal surface and no other vertical forces are acting i e f n mg where m is the object s mass and g is the acceleration due to gravity. Example friction force the friction force of a 100 lb wooden crate pushed across a concrete floor with friction coefficient of 0 62 can be calculated as. μ static μ s or kinetic μ k frictional coefficient.
1 1 1 1 1 1 10 100 ft 10 6 10 5 10 4 10 3 10 2 10 1 10 0 10 1 m e y e r e h e. For example static friction can prevent an object from sliding down a sloped surface. The coefficient of static friction typically denoted as μ s is usually higher than the coefficient of kinetic friction. Rubber wet asphalt 0 25 0 751 rubber dry concrete 0 6 0 851 rubber wet concrete 0 45 0 751 silver silver 1 4 0 55.