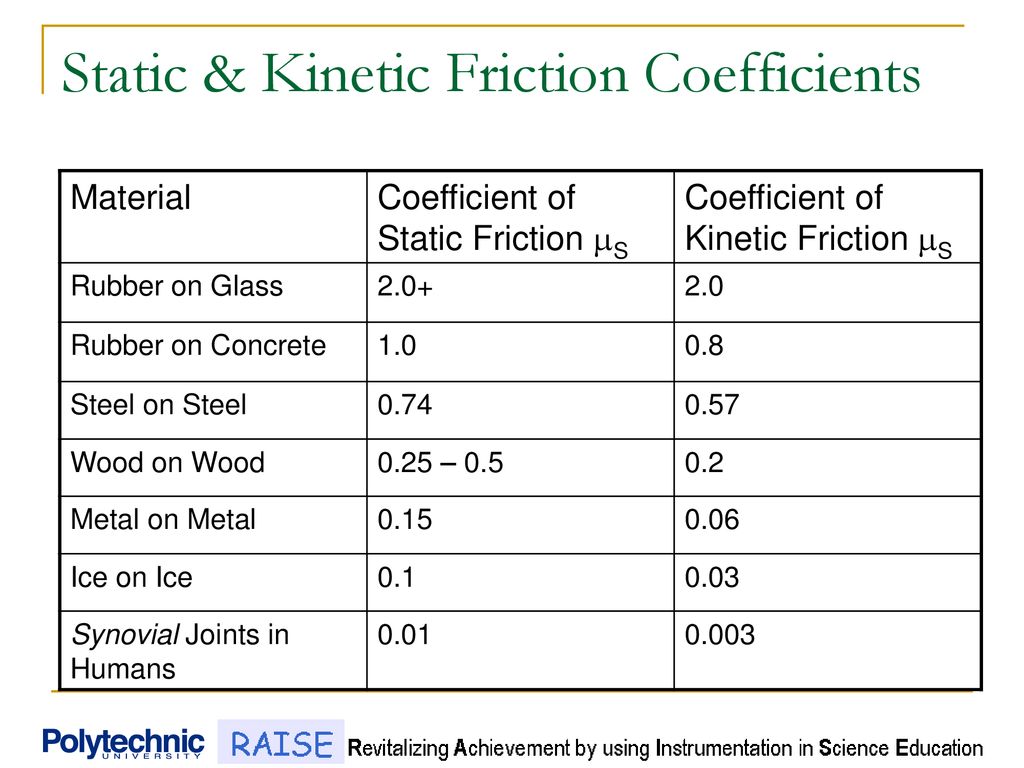
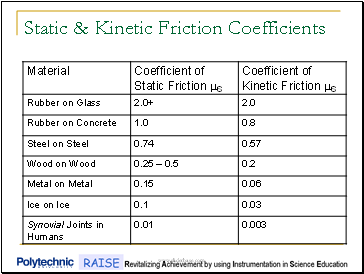
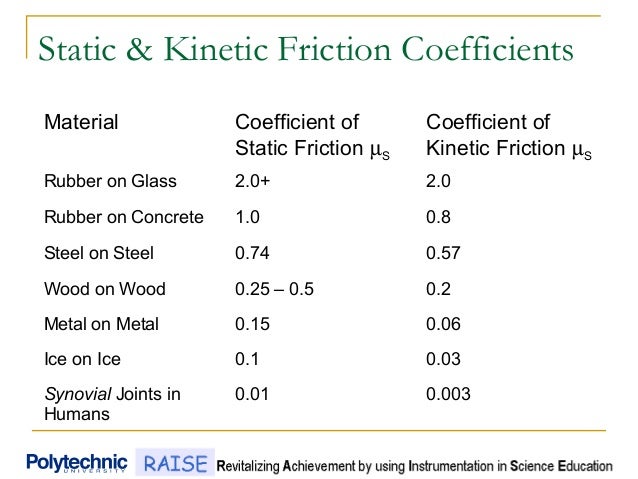
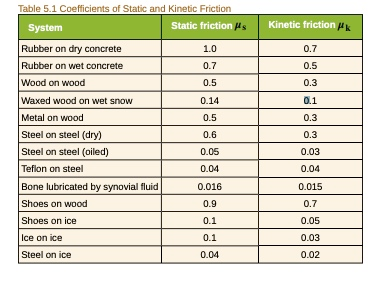
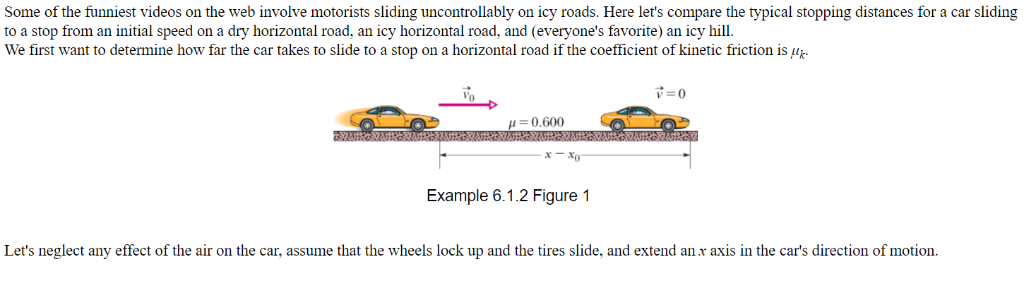
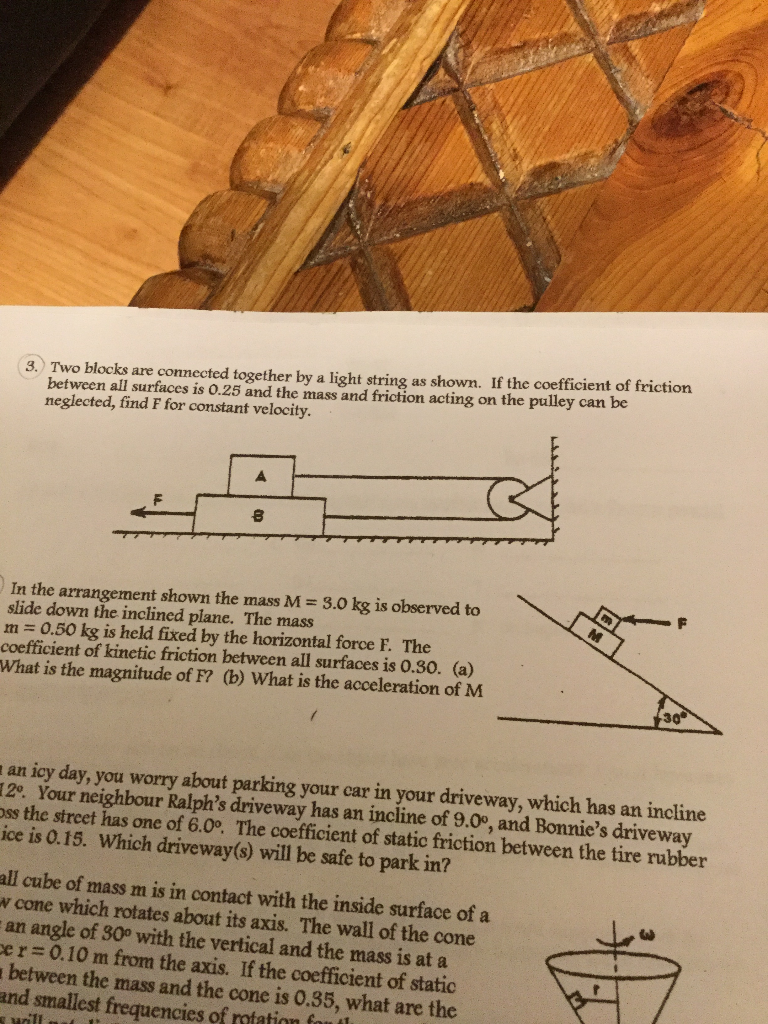
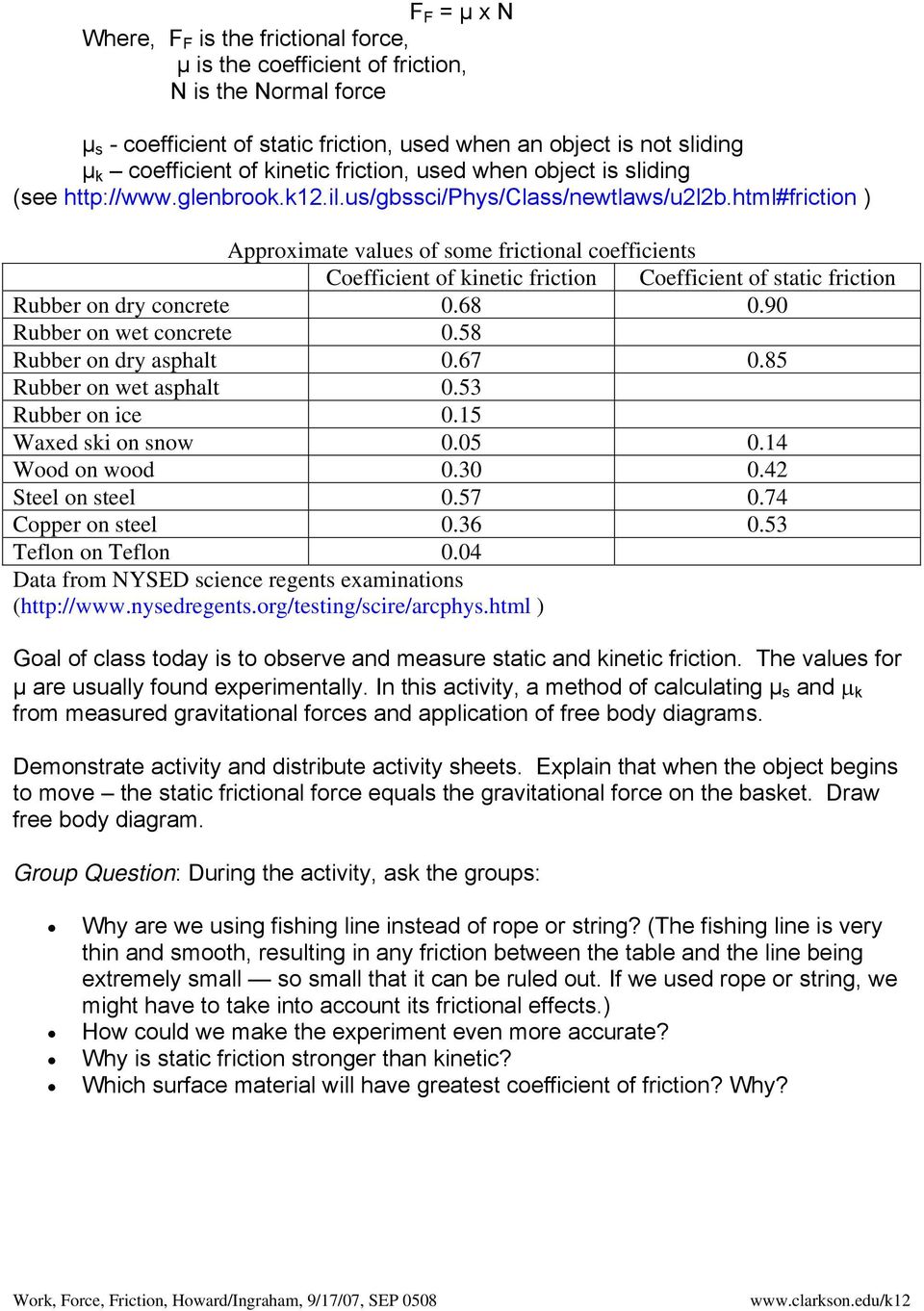
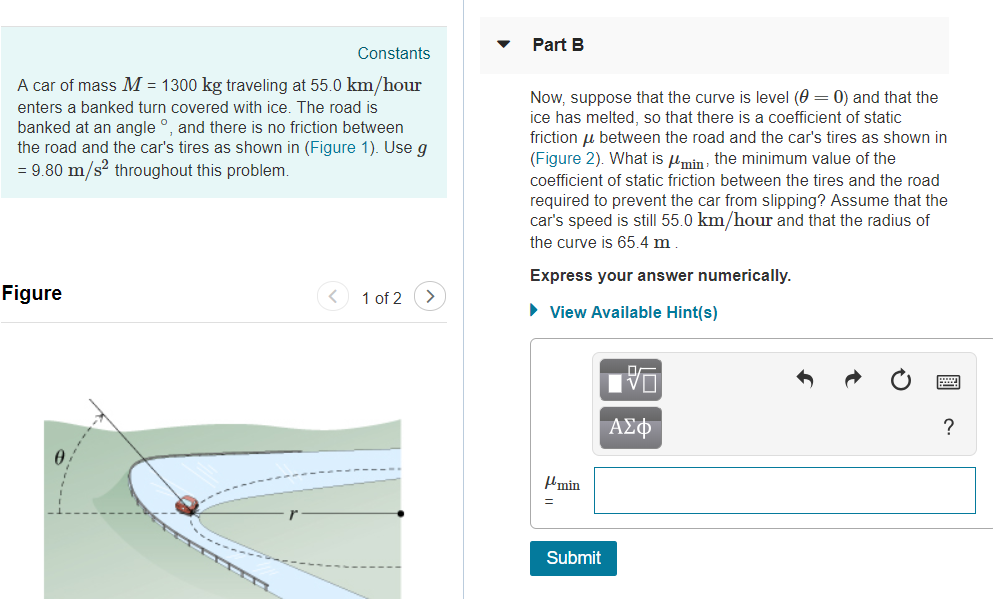
Coefficient Of Kinetic Friction Rubber On Ice

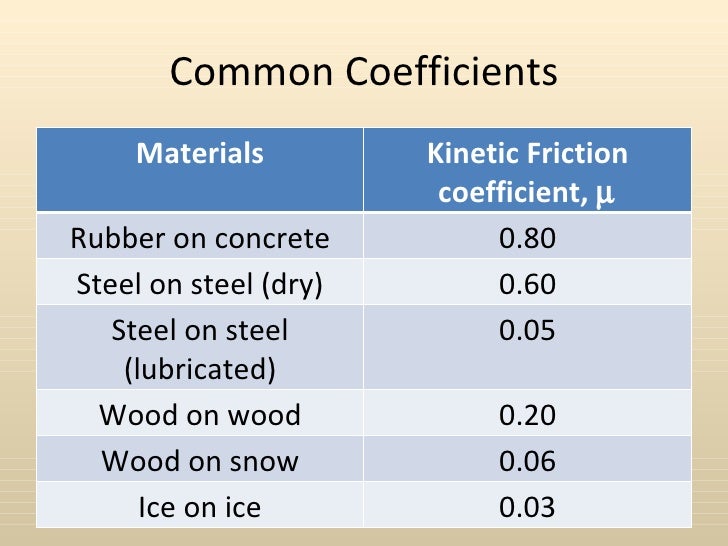
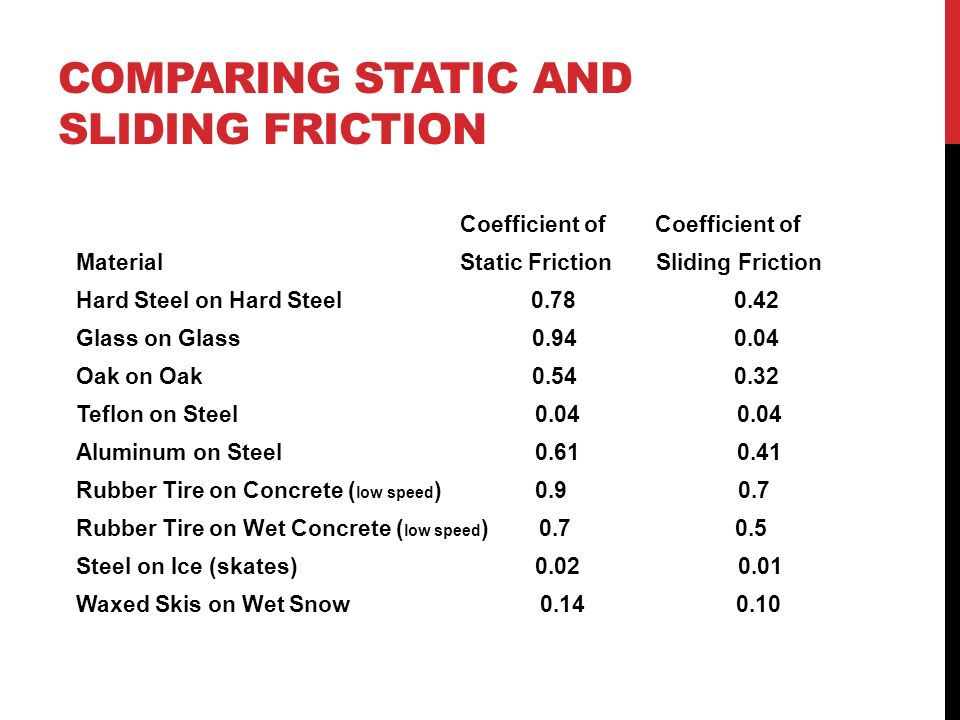
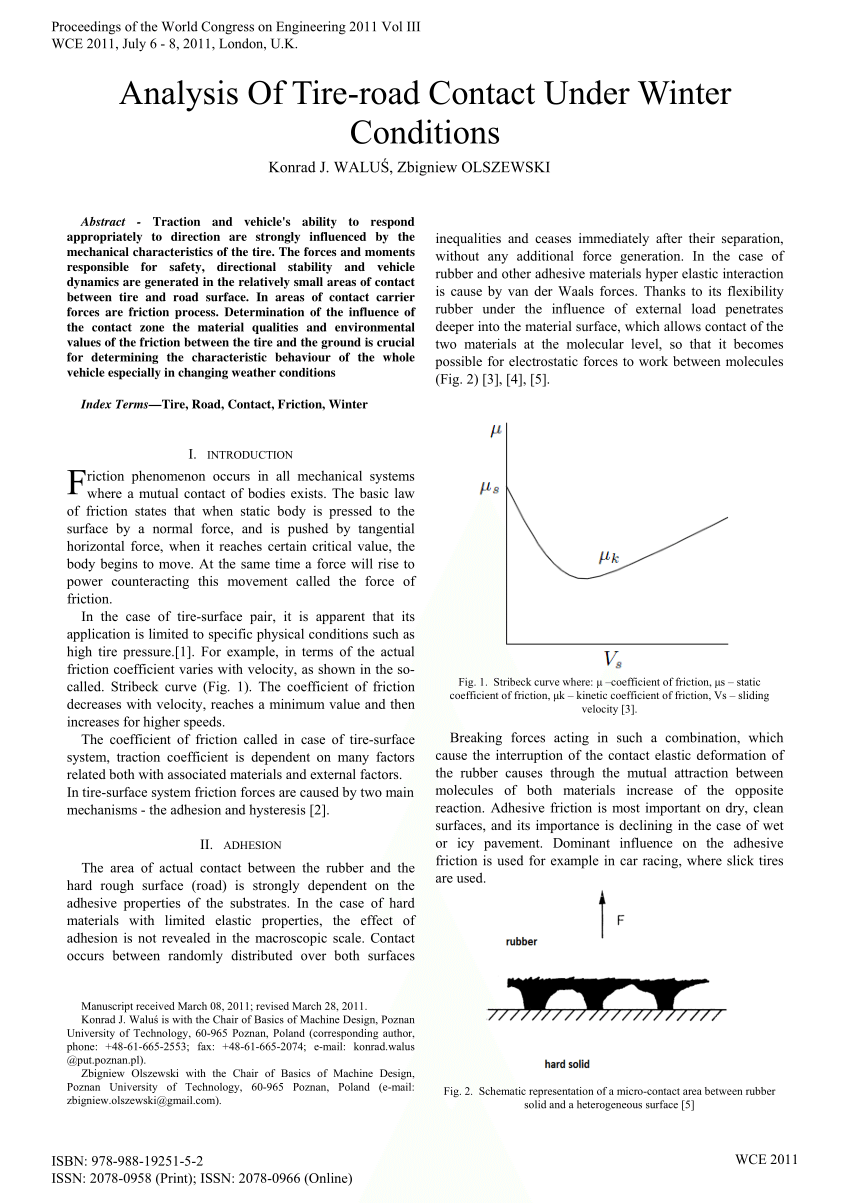
μ static μ s or kinetic μ k frictional coefficient.
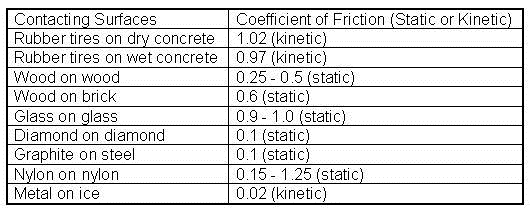
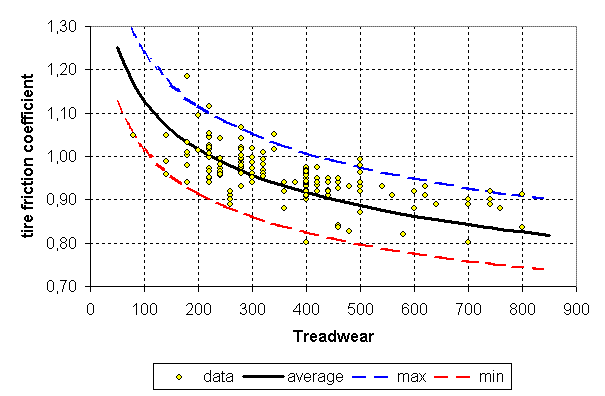
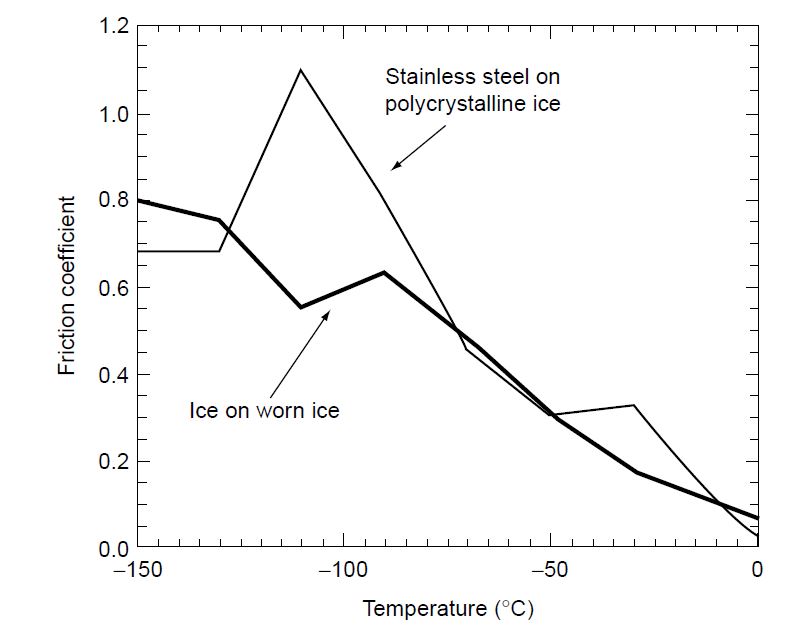
Coefficient of kinetic friction rubber on ice. The distance s travelled by the skate frame catapulted on the ice surface showed maximum around 1 to 2 c as shown in figure 10a. The coefficient of static friction typically denoted as μ s is usually higher than the coefficient of kinetic friction. Approximate coefficients of friction. Experimentally obtaining values for the total distance traveled and for the initial velocity of the curling stone with the aid of nih imaging we calculate the coefficient of kinetic friction for curling ice.
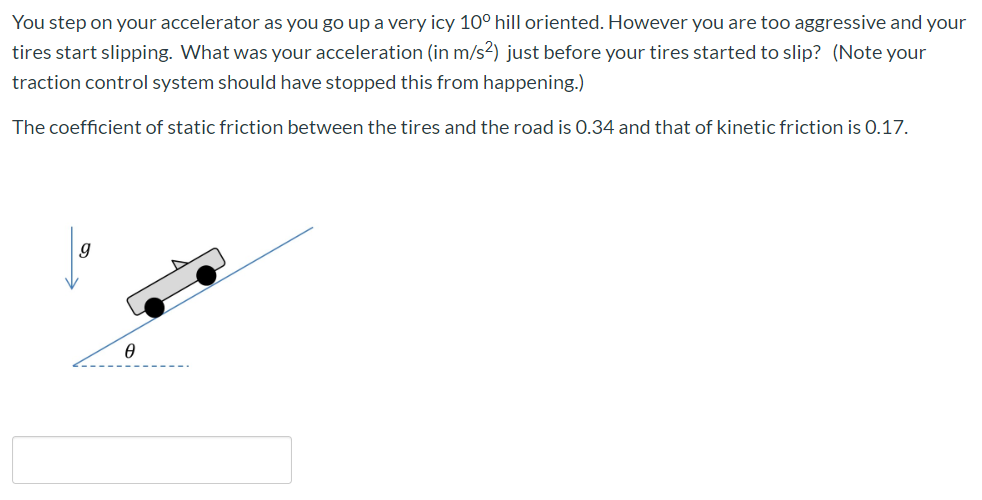
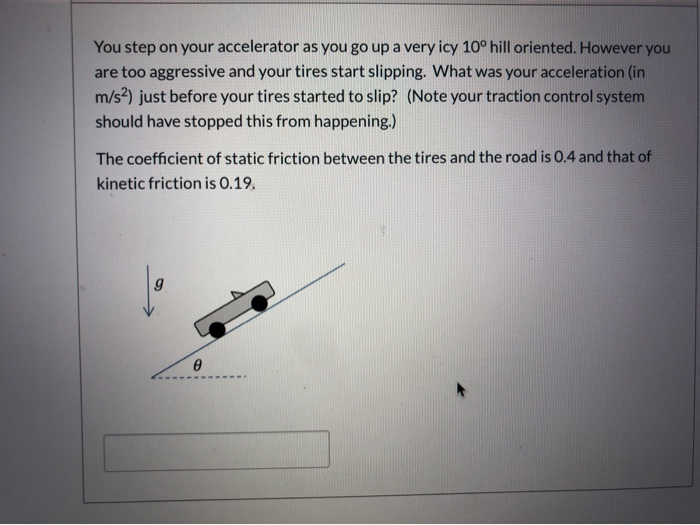
From wikibooks open books for an open world. The coefficient of kinetic friction for curling ice. For example static friction can prevent an object from sliding down a sloped surface. Rubber on concrete wet 0 58 rubber on asphalt dry.
F f frictional force n lb. For this wall puck friction the magnitude of the frictional force depends on the normal force for the wall pushing on the puck to make it turn. But it gets even more complicated. N normal force between the surfaces n lb there are at least two types of friction forces.
The friction force is the force exerted by a surface when an object moves across it or makes an effort to move across it. Of course the coefficient of friction between the rubber puck and the wall would likely be much higher than for the ice rubber interaction. F f μ n 1. Rubber on concrete dry 0 68.
Static friction is friction between two or more solid objects that are not moving relative to each other.