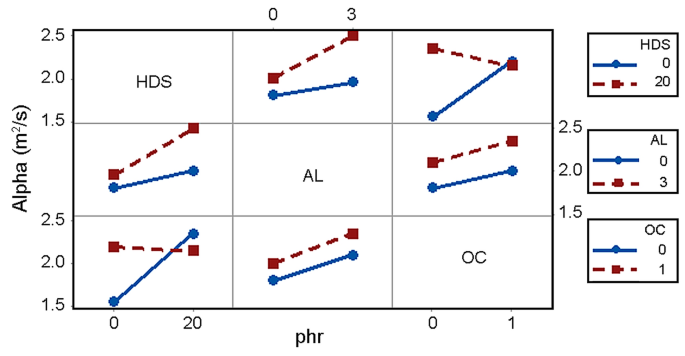
Coefficient Of Thermal Conductivity Of Rubber
Thermal conductivity w.
Coefficient of thermal conductivity of rubber. For example materials that conduct heat very well such. 2012 manipulated the curing process to produce rubber samples that had been produced with different vulcanization rate. Lasance articles design materials compounds adhesives substrates test measurement elastomer rubber technical data thermal conductivity in the may 2001 issue this column discussed the thermal conductivity of unfilled plastics. November 1 2001 clemens j.
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to conduct heat it is commonly denoted by or. To determine the coefficient of thermal conductivity of a bad conductor using lee s disc apparatus. It has inlet and outlet tubes for steam. The chemical phase of the material.
An uncured sample was also obtained for use as a reference. In addition it has radial holes to insert thermometers. Thermal conductivity is a material property that describes ability to conduct heat thermal conductivity can be defined as the quantity of heat transmitted through a unit thickness of a material in a direction normal to a surface of unit area due to a unit temperature gradient under steady state conditions. M k and also an interface heat transfer coefficient which has w m 2 k.
Crc rubber 92 nd 0 16 griffiths natural rubber 1923 0 134 hayes synthetic rubbers 1960 thiokel st 0 268 kel f 3700 0 117 0 113. Lee s disc apparatus consist of a metallic disc resting on a 5 cm deep hollow cylinder steam chamber of same diameter. Conductivity σ x 10 7 ωm. Thermal conductivity is analogous to electrical conductivity.
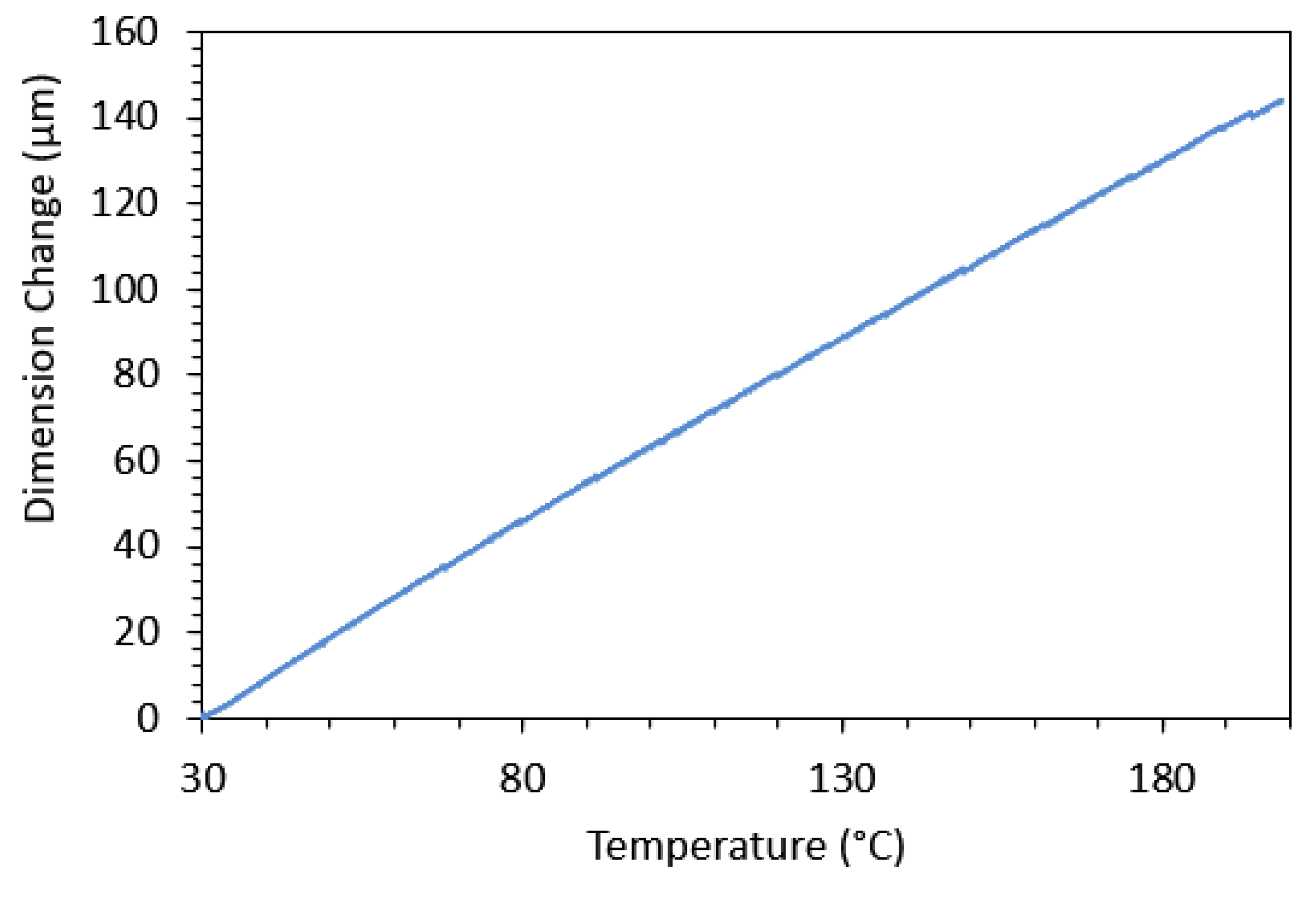
Similarly thermal resistance is the inverse of thermal conductivity as electrical resistance is the inverse of electrical conductivity. When the phase of a material changes an abrupt change in its heat conductivity may arise. Resistivity ρ ohm m temperature coefficient α per degree c. Coefficient of expansion is the rate at which a material will grow in length with an increase in temperature.
Effect on thermal conductivity. The coefficient of thermal conductivity or k is different for each material and defines how good the material is as a thermal conductor.