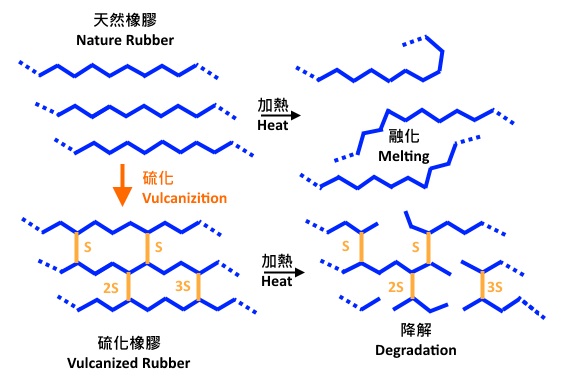
Crosslink Density Of Vulcanized Rubber

Bimodal crosslink distributions are prevalent in radically cured systems 12 25 29 30 31.
Crosslink density of vulcanized rubber. Vulcanization and reinforcement are two important factors contributing to the properties of vulcanized rubber. The crosslink density for rubber is one of the most influential parameters on the physical mechanical and. Determination of crosslink density of rubber and other polymers physical crosslinking chemical crosslinking quality control of polymer products quality inspection of polymer aging process rubber vulcanization process and formulation research determination of moisture content and moisture distribution in the solid matrix. The natural rubber mixture prepared in this context was vulcanized for 3 5 10 and 15 minutes at a constant temperature of 160 c.
The elastic force of retraction elasticity is directly proportional to the crosslink density. In addition to that the effects of the crosslink density on the mechanical. Crosslink density is defined as the number of crosslink points per unit volume. The crosslink density of each vulcanizite was determined by equilibrium swelling tests and the flory rehner equation.
In order to investigate the influence of carbon black cb on chemical crosslinking three groups of samples with different crosslink densities were prepared. The chemical interaction between sulfur and rubber is called crosslink. These conditions will determine the flexibility behaviors of the final rubber. Crosslink density is used to measure the degree of crosslinking between rubber and sulfur.
For all four vulcanization systems the crosslink density is represented by a monodistribution which is normally expected with sulfur based systems. The study on influence of total crosslink density on shore a hardness and 300 modulus of nr vulcanizates showed that they both increased linearly with the crosslink density the slopes were 2 7 3 0 cm 3 10 5 mol and 0 27 0 31 mpa cm 3 10 5 mol for shore a hardness and 300 modulus respectively whether the crosslink density. The value of crosslink density may be in the order of 10 3 to 10 5 mol cm 3 for a typical rubber material corresponding to 15 to 1500 monomer units between the crosslinks. Cross link density is proportional to the stiffness of the rubber.
The first region is the induction. The vulcanising agent originally referred to was elemental. The degree of crosslinking is affected by temperature pressure and the time of heating time. Therefore oscillating disk or moving die rheometry are popular techniques in the kinetics of rubber vulcanization bateman et al 1963.
A typical rheometer chart of the accelerated sulphur vulcanization process is illustrated in fig.